Mechanical Behavior of Materials
Experimental characterization of the mechanical behavior of metallic and composite materials under static, quasi-static and dynamic loads is one of the most important research sectors of LTSM. The specific activities of LTSM in this area are the following:
Mechanical behavior under quasi-static loads (tension, compression, bending, torsion, buckling, fracture toughness, etc)
Fatigue
-
Derivation of S-N curves and fatigue crack-growth curves,
-
Effect of overloads and load interaction on the fatigue crack growth,
-
Effect of alloy ingredients on fatigue crack growth, and
-
Effect of microstructure on fracture behavior.
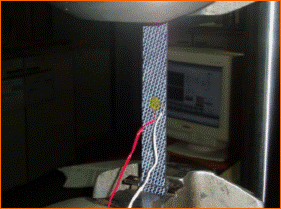
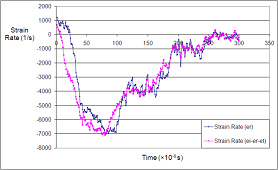
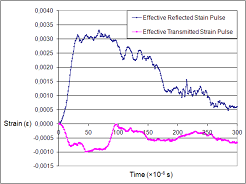
High-strain rate mechanical tests (split Hopkinson bars)
Non-destructive testing and metallographic characterization
- Hardness test,
- Ultrasound inspection,
- Metallographic characterization,
- Fractographic analysis, and
- Corrosion characterization.
High temperature testing
- Creep tests, and
- Testing in environmental chamber.
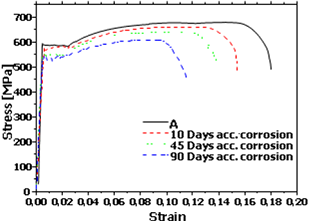
Corrosion tests
- Exposure to atmospheric corrosion,
- Tests with caustic spray,
- Split-up under tension and corrosion.
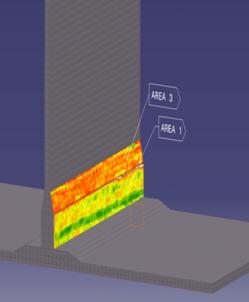
3-point bending test in a composite bonded joint
Split Hopkinson tests
| Effect of corrosion on the mechanical properties of metallic bars used as concrete reinforcements | C-scan image of an adhesively bonded joint between composite plates |